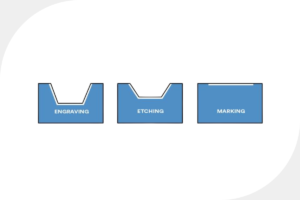
Laser Engraving – High Depth:
This method involves the physical removal of material by heating and vaporizing the metal surface using a laser. It is ideal for high-wear environments, whether physical or highly corrosive. Print visibility is highly resistant due to the need to remove several layers of the surface to achieve the desired engraving depth.
Laser Etching – Medium Depth:
This is a subcategory of engraving that also removes material but only at the surface level. This results in a very shallow mark (<0.001″) and is less durable than high-depth laser engraving.
Types of Laser Marking
What is Laser Engraving?
Laser engraving involves material removal through high temperatures generated by a laser. It directs heat to the material surface, creating deep cracks in the desired pattern. This produces a permanent, high-contrast mark that remains readable even after wear or surface treatments. It is ideal for creating long-lasting cuts in a wide variety of materials, especially in applications where identification information needs to endure for years, even in challenging conditions such as exposure to aggressive chemicals, moisture, and dirt. This method facilitates reading laser-engraved data plates, even on industrial equipment parts, thanks to the high contrast provided by this laser marking technique.
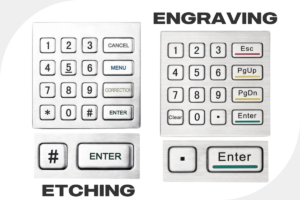
Laser Engraving and Laser Etching:
Although the terms laser engraving and laser etching are used interchangeably, they are different methods with different depths in cuts. Laser engraving is deeper and alters the material’s shape, while Laser Etching is shallower and does not change the material’s shape. Both methods can be used together to provide additional contrast. For example, in the case of particularly dark metals, engraving may not be dark enough to provide the necessary contrast and readability. Etching can add clearer marks to the unengraved part to increase contrast.
- Different Principles:
In general, laser engraving uses a laser beam to achieve localized vaporization of the material surface, while etching involves a redox reaction between substances to achieve metal dissolution.
- Different Effects:
In the current process, laser engraving on many metallic materials and certain dense substances often does not achieve the desired depth and is superficial. Meanwhile, etching on metal can achieve the desired depth and combine with the painting process for a multicolor finish.
- Different Application Scope:
Laser engraving is more widely applicable, as most materials can be laser-engraved or laser-marked, while etching is limited to metals, stone, among others.
- Different Processes:
The laser engraving process is simple and has fewer steps, while the etching process is more complex and detailed.
- Different Production Efficiency:
Laser engraving is suitable for engravings or marks in small quantities, while etching is more suitable for large-scale production.
- Different Precision:
In general, etching has higher precision, and combined with photolithography, achieving lines of up to 0.01 mm is not a problem.
sales@logicbus.com | support@logicbus.com | +1 619 616 7350 | Start conversation