In the RF communication industry, it is common to hear the terms vertical, horizontal or circular polarization, and often as we go deeper into this type of technology we see that there are different antennas with different polarizations, and it may be the case that we do not know which one to use for your project or application. Each polarization has its own characteristics and disadvantages, and it is good to know how each of them works to know which one is the best for your application
To begin with, what does the term polarization mean?
In electromagnetism, there is a concept that describes one of the main characteristics of electromagnetic waves and plays an important role in radio frequency identification (RFID): electromagnetic polarization. Polarization is a characteristic of transverse waves that describes the orientation of their oscillation.
It must be understood that an electromagnetic wave is a type of wave that travels through space and carries energy. Electromagnetic waves are made up of an electric and a magnetic field and can manifest themselves as visible light, thermal radiation such as heat, radio waves, infrared light, X-rays, ultraviolet light, etc. Generally these waves are made up of several waves of different oscillation orientations, and when this occurs they are known as non-polarized electromagnetic waves. When some of these waves pass through a surface or are reflected, they tend to lose some of these waves to have only waves of a single type of oscillation orientation, and these are known as polarized electromagnetic waves.

When a wave is polarized it can only be detected or visualized in a specific position or medium. For example, there are polarizing light filters that only let light go up to a certain level since it only lets a specific type of wave go through. Depending on the type of filter or surface where the light is reflected, one type of polarization will occur.
There are 3 types of polarization in electromagnetic waves: Linear, circular and elliptical polarization. Linear polarization is a type of wave propagation in which the orientation of the electric field oscillation is straight in a plane, i.e. the wave oscillates linearly (blue wave) as can be seen in the following image. This type of polarization can have variants depending on the magnitude of its components, but the most common are vertical and horizontal polarization, i.e. the wave travels in a horizontal or vertical plane in the direction of the wave trajectory.
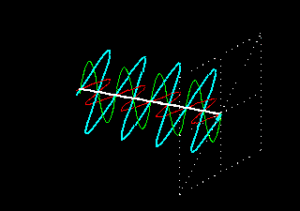
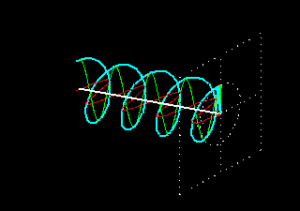
Circular polarization occurs when the components of the wave are of equal magnitude and this creates a circular oscillation motion. Elliptical polarization occurs when the components of the wave are of different magnitude, which creates an elliptical trajectory. This is the most common form of waves as it is only created with a difference in magnitude which occurs very commonly in nature.
Seeing that there are different types of polarization and that each describes how the direction of a wave behaves, we can now move on to see how this relates to RFID technology.
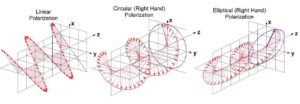
Types of polarization used in RFID
An RFID system consists of 2 main components: a reader and a tag. RFID tags are electronic devices consisting of an antenna, a chip and an enclosure. The chip usually contains a memory where a unique code that identifies the tag is stored. This chip is connected to an antenna which sends the code by radio waves. The RFID reader is the electronic device that captures the code coming from the tag and processes it to send it to a system or software. The reader needs an antenna to be able to receive the tag code, and this is where the use of antennas of different polarizations comes into play.
The antennas used by the RFID reader are usually of 3 different types: Vertical, horizontal and circular polarization antennas. Both vertically and horizontally polarized antennas are antennas that pick up linearly polarized radio wave signals. Vertically polarized antennas can “only” receive a vertically polarized signal at a certain distance but could not receive a horizontally polarized signal, and vice versa. Circularly polarized antennas can receive circularly polarized signals from any direction.
Applications of Radio Wave Polarization in RFID
Our radio frequency device supplier RFID Inc. offers a wide variety of antennas for different types of systems and applications. From low frequency antennas (125 KHz) to ultra high frequency antennas (915 MHz).
UHF RFID antennas are usually used for high range applications such as toll stations and access control in buildings. RFID Inc. UHF antennas can be found in 3 different polarizations, but how do I know which type of antenna polarization I need for my application?
We can start with linear antennas, i.e. vertical and horizontal antennas.
Linearly polarized antennas:
- They direct and concentrate the radio waves in a single plane, so the transmission will be stable and with long range but the tag needs to be perfectly aligned with the antenna so it does not lose signal.
- They are suitable for applications where high stability is needed and where the position of the tag will be stable.
- They are simple and inexpensive, easy to repair.
- They are commonly used in portable radios, toll systems, facility access control, etc.
Circularly polarized antennas are a little more complicated as they oscillate in a non-linear path.
Circularly polarized antennas:
- Have a circular trajectory that can read tags in different positions and inclinations, but its range is reduced.
- Are immune to interference, so it is ideal for use in places with trees, buildings or a closed environment.
- They are suitable for applications where the inclination and position of the tag is unpredictable.
- They are commonly used in satellites, moving object detection, drones, etc.


At Logicbus, we handle antennas for linear and circular polarized RFID systems, perfect for all types of projects and applications.
Visit our website:
www.logicbus.com




sales@logicbus.com | support@logicbus.com | +1 619 616 7350 | Start conversation

