As the manufacturing world becomes more integrated with automated technology, it’s important to understand how this technology can assist you. Industrial automation can make life easier for those working on the production floor and help increase a company’s productivity. One type of device that aids workers is known as photoelectric sensors.
Photoelectric sensors come in many different forms and can be used in various industries to perform a diverse range of tasks. To understand what a photoelectric sensor is and determine the best sensor for a particular application, here’s a breakdown of its functionality.
What is a Photoelectric Sensor?
A photoelectric sensor is a device that detects a difference in the level of light received from the light source. The sensor is composed of a light source, an amplifier, a signal converter, and an output.
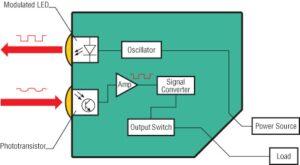
Three Types of Photoelectric Sensors
There are three main types of photoelectric sensors: through-beam, retroreflective, and diffuse. Each sensor has its own strengths and can be used in various ways.
Thru-Beam
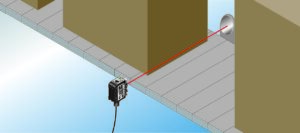
In through-beam detection, also known as opposed mode, two separate devices are used to establish or interrupt a beam. One sensor houses the light emitter, while the other houses the receiver. A through-beam sensor detects objects when an object interrupts the light beam between the two sensors.


Through-beam sensors can be used to:
- Detect very small objects.
- Monitor fill levels within containers.
- Detect overlapped or stacked materials.
- Determine the precise location of a specific object.
- Identify the content of a container.
- Detect opaque objects.
The advantages of using a through-beam sensor are that it is the most accurate type of sensor and has the longest detection range of the three. They are also the best choice when used in a dirty environment. It’s important to note that at least two separate parts need to be installed for this device to function correctly.
Retroreflective
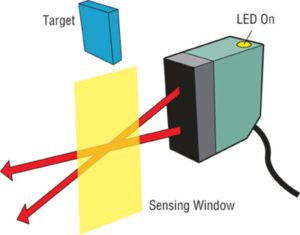
In retroreflective detection, both the light source and the receiving device are housed in the same casing. The sensor works in conjunction with a reflector. The light emitted from the sensor is directed to the reflector, which then sends it back to the light-receiving element. The sensor detects the presence of an object when the path of light is interrupted.
In addition to retroreflective detection, there is polarized retroreflective detection. Polarized retroreflective detection features a polarized optical block that reduces glare response from a “hot spot” on a shiny surface of the detected object.

Retroreflective sensors can be used to:
- Detect large objects.
- Detect objects moving at high speeds.
- Identify reflective tape at high speeds.
- Detect a transparent glass or plastic product.
Retroreflective sensors are a more cost-effective and slightly less accurate option than through-beam sensors. When working with transparent or clear products, retroreflective sensors are the better choice. Another advantage is that retroreflective sensors only require wiring on one side, whereas through-beam sensors require wiring on both sides of the device.
Diffuse
In optical proximity detection, also known as diffuse sensing, the light source and the receiver are housed in the same device. Diffuse sensors detect objects when the light beam, emitted towards the target, is reflected back to the sensor by the target. What makes diffuse sensors an excellent choice for automation is that they are more compact than typical units since all components are in a single casing.
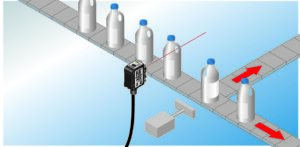
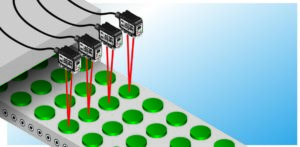
Diffuse sensors can be used to:
- Detect multiple objects in a common conveyor system.
- Identify translucent objects.
- Measure the fill level within containers.
- Detect the presence of pieces, boxes, and roll materials.
- Identify specific identifying features to determine the orientation of an object.
- Detect unwanted conditions for product inspection tasks.
Diffuse sensors are the easiest to install because everything is included in a single device and provide a cost-effective detection solution. The disadvantages of diffuse sensors are that they are less accurate in position detection than through-beam and retroreflective sensors, and they are not as effective on translucent objects. Additionally, these sensors can be most affected by color, texture, incidence angle, target characteristics, and dirty environments.




sales@logicbus.com | support@logicbus.com | +1 619 616 7350 | Start conversation

